Ministry of Finance Shares Highlights Of The Union Budget 2024-25
The Union Minister of Finance and Corporate Affairs Smt. Nirmala Sitharaman presented the Union Budget 2024-25 in Parliament today. The highlights of the budget are as follows:
Part-A
Budget Estimates 2024-25:
-
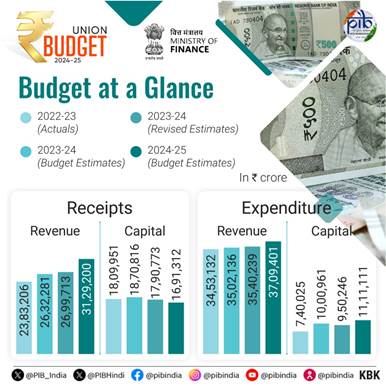
- Total receipts other than borrowings: `32.07 lakh crore.
- Total expenditure: `48.21 lakh crore.
- Net tax receipt: `25.83 lakh crore.
- Fiscal deficit: 4.9 per cent of GDP.
- Government aims to reach a deficit below 4.5 per cent next year.
- Inflation continues to be low, stable and moving towards the 4% target; Core inflation (non-food, non-fuel) at 3.1%.
- The focus of budget is on EMPLOYMENT, SKILLING, MSMEs, and the MIDDLE CLASS.
Package of PM’s five schemes for Employment and Skilling
- Prime Minister’s Package of 5 Schemes and Initiatives for employment, skilling and other opportunities for 4.1 crore youth over a 5-year period.
- Scheme A – First Timers: One-month salary of up to `15,000 to be provided in 3 installments to first-time employees, as registered in the EPFO.
- Scheme B – Job Creation in manufacturing: Incentive to be provided at specified scale directly, both employee and employer, with respect to their EPFO contribution in the first 4 years of employment.
- Scheme C – Support to employers: Government to reimburse up to `3,000 per month for 2 years towards EPFO contribution of employers, for each additional employee.
- New centrally sponsored scheme for Skilling
- 20 lakh youth to be skilled over a 5-year period.
- 1,000 Industrial Training Institutes to be upgraded in hub and spoke arrangements.
- New Scheme for Internship in 500 Top Companies to 1 crore youth in 5 years
Nine Budget Priorities in pursuit of ‘Viksit Bharat’:
-
- Productivity and resilience in Agriculture
- Employment & Skilling
- Inclusive Human Resource Development and Social Justice
- Manufacturing & Services
- Urban Development
- Energy Security
- Infrastructure
- Innovation, Research & Development and
- Next Generation Reforms
Priority 1: Productivity and resilience in Agriculture
- Allocation of `1.52 lakh crore for agriculture and allied sectors.
- New 109 high-yielding and climate-resilient varieties of 32 field and horticulture crops to be released for cultivation by farmers.
- 1 crore farmers across the country to be initiated into natural farming, with certification and branding in next 2 years.
- 10,000 need-based bio-input resource centres to be established for natural farming.
- Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI) for Agriculture to be implemented for coverage of farmers and their lands in 3 years.
Priority 2: Employment & Skilling
- As part of the Prime Minister’s package, 3 schemes for ‘Employment Linked Incentive’ to be implemented – Scheme A – First Timers; Scheme B – Job Creation in manufacturing; Scheme C – Support to employers.
- To facilitate higher participation of women in the workforce,
- working women hostels and crèches to be established with industrial collaboration
- women-specific skilling programmes to be organized
- market access for women SHG enterprises to be promoted
Skill Development
- New centrally sponsored scheme for Skilling under Prime Minister’s Package for 20 lakh youth over a 5-year period.
- Model Skill Loan Scheme to be revised to facilitate loans up to
`7.5 lakh. - Financial support for loans upto `10 lakh for higher education in domestic institutions to be provided to youth who have not been eligible for any benefit under government schemes and policies.
Priority 3: Inclusive Human Resource Development and Social Justice
Purvodaya
- Industrial node at Gaya to be developed along the Amritsar-Kolkata Industrial Corridor.
- Power projects, including new 2400 MW power plant at Pirpainti, to be taken up at a cost of `21,400 crore.
Andhra Pradesh Reorganization Act
-
-
- Special financial support through multilateral development agencies of `15,000 crore in the current financial year.
- Industrial node at Kopparthy along Vishakhapatnam-Chennai Industrial Corridor and at Orvakal along Hyderabad-Bengaluru Industrial Corridor.
-
Women-led development
- Total allocation of more than `3 lakh crore for schemes benefitting women and girls.
Pradhan Mantri Janjatiya Unnat Gram Abhiyan
- Socio-economic development of tribal families in tribal-majority villages and aspirational districts, covering 63,000 villages benefitting 5 crore tribal people.
Bank branches in North-Eastern Region
- 100 branches of India Post Payment Bank to be set up in the North East region.
Priority 4: Manufacturing & Services
Credit Guarantee Scheme for MSMEs in the Manufacturing Sector
- A credit guarantee scheme without collateral or third-party guarantee in term loans to MSMEs for purchase of machinery and equipment.
Credit Support to MSMEs during Stress Period
- New mechanism to facilitate continuation of bank credit to MSMEs during their stress period.
Mudra Loans
- The limit of Mudra loans under ‘Tarun’ category to be enhanced to `20 lakh from `10 lakh for those who have successfully repaid previous loans.
Enhanced scope for mandatory onboarding in TReDS
- Turnover threshold of buyers for mandatory onboarding on the TReDS platform to be reduced from `500 crore to `250 crore..
MSME Units for Food Irradiation, Quality & Safety Testing
- Financial support to set up 50 multi-product food irradiation units in the MSME sector .
E-Commerce Export Hubs
- E-Commerce Export Hubs to be set up under public-private-partnership (PPP) mode for MSMEs and traditional artisans to sell their products in international markets.
Critical Mineral Mission
- Critical Mineral Mission to be set up for domestic production, recycling of critical minerals, and overseas acquisition of critical mineral assets.
Offshore mining of minerals
- Auction of the first tranche of offshore blocks for mining, building on the exploration already carried out.
Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI) Applications
- Development of DPI applications in the areas of credit, e-commerce, education, health, law and justice, logistics, MSME, services delivery, and urban governance.
Priority 5: Urban Development
Transit Oriented Development
- Formulation of Transit Oriented Development plans and strategies to implement and finance 14 large cities above 30 lakh population.
Urban Housing
- Investment of `10 lakh crore, including the central assistance of `2.2 lakh crore in next 5 years, under PM Awas Yojana Urban 2.0 proposed to address the , housing needs of 1 crore urban poor and middle-class families.
Street Markets
- New scheme to support the development of 100 weekly ‘haats’ or street food hubs every year for the next 5 years in select cities.
Priority 6: Energy Security
Energy Transition
- Policy document on ‘Energy Transition Pathways’ to balance the imperatives of employment, growth and environmental sustainability to be brought out.
Pumped Storage Policy
- Policy for promoting pumped storage projects for electricity storage to be brought out.
Research and development of small and modular nuclear reactors
- Government to partner with private sector for R&D of Bharat Small Modular Reactor and newer technologies for nuclear energy, and to set up Bharat Small Reactors.
Advanced Ultra Super Critical Thermal Power Plants
- Joint venture proposed between NTPC and BHEL to set up a full scale 800 MW commercial plant using Advanced Ultra Super Critical (AUSC) technology.
Roadmap for ‘hard to abate’ industries
- Appropriate regulations for transition of ‘hard to abate’ industries from the current ‘Perform, Achieve and Trade’ mode to ‘Indian Carbon Market’ mode to be put in place.
Priority 7: Infrastructure
Infrastructure investment by Central Government
- `11,11,111 crore (3.4 % of GDP) to be provided for capital expenditure.
Infrastructure investment by state governments
- Provision of `1.5 lakh crore for long-term interest free loans to support states in infrastructure investment.
Pradhan Mantri Gram SadakYojana (PMGSY)
- Launch of phase IV of PMGSY to provide all-weather connectivity to 25,000 rural habitations.
Irrigation and Flood Mitigation
- Financial support of `11,500 crore to projects such as the Kosi-Mechi intra-state link and other schemes in Bihar.
- Government to provide assistance to Assam, Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand and Sikkim for floods, landslides and other related projects.
Tourism
- Comprehensive development of Vishnupad Temple Corridor, Mahabodhi Temple Corridor and Rajgir.
- Assistance for development of temples, monuments, craftsmanship, wildlife sanctuaries, natural landscapes and pristine beaches of Odisha.
Priority 8: Innovation, Research & Development
- Anusandhan National Research Fund for basic research and prototype development to be operationalised.
- Financing pool of `1 lakh crore for spurring private sector-driven research and innovation at commercial scale.
Space Economy
- Venture capital fund of `1,000 crore to be set up for expanding the space economy by 5 times in the next 10 years.
Priority 9: Next Generation Reforms
Rural Land Related Actions
- Unique Land Parcel Identification Number (ULPIN) or Bhu-Aadhaar for all lands
- Digitization of cadastral maps
- Survey of map sub-divisions as per current ownership
- Establishment of land registry
- Linking to the farmers registry
Urban Land Related Actions
- Land records in urban areas to be digitized with GIS mapping.
Services to Labour
- Integration of e-shram portal with other portals to facilitate such one-stop solution.
- Open architecture databases for the rapidly changing labour market, skill requirements and available job roles.
- Mechanism to connect job-aspirants with potential employers and skill providers.
NPS Vatsalya
- NPS-Vatsalya as a plan for contribution by parents and guardians for minors.
PART B
Indirect Taxes
GST
- Buoyed by GST’s success, tax structure to be simplified and rationalised to expand GST to remaining sectors.
Sector specific customs duty proposals
Medicines and Medical Equipment
- Three cancer drugs namely TrastuzumabDeruxtecan, Osimertinib and Durvalumab fully exempted from custom duty.
- Changes in Basic Customs Duty (BCD) on x-ray tubes & flat panel detectors for use in medical x-ray machines under the Phased Manufacturing Programme.
Mobile Phone and Related Parts
- BCD on mobile phone, mobile Printed Circuit Board Assembly (PCBA) and mobile charger reduced to 15 per cent.
Precious Metals
- Customs duties on gold and silver reduced to 6 per cent and that on platinum to 6.4 per cent.
Other Metals
- BCD removed on ferro nickel and blister copper.
- BCD removed on ferrous scrap and nickel cathode.
- Concessional BCD of 2.5 per cent on copper scrap.
Electronics
- BCD removed, subject to conditions, on oxygen free copper for manufacture of resistors.
Chemicals and Petrochemicals
- BCD on ammonium nitrate increased from 7.5 to 10 per cent.
Plastics
- BCD on PVC flex banners increased from 10 to 25 per cent.
Telecommunication Equipment
- BCD increased from 10 to 15 per cent on PCBA of specified telecom equipment.
Trade facilitation
- For promotion of domestic aviation and boat & ship MRO, time period for export of goods imported for repairs extended from six months to one year.
- Time-limit for re-import of goods for repairs under warranty extended from three to five years.
Critical Minerals
- 25 critical minerals fully exempted from customs duties.
- BCD on two critical minerals reduced.
Solar Energy
- Capital goods for use in manufacture of solar cells and panels exempted from customs duty.
Marine products
- BCD on certain broodstock, polychaete worms, shrimp and fish feed reduced to 5 per cent.
- Various inputs for manufacture of shrimp and fish feed exempted from customs duty.
Leather and Textile
- BCD reduced on real down filling material from duck or goose.
- BCD reduced, subject to conditions, on methylene diphenyl diisocyanate (MDI) for manufacture of spandex yarn from 7.5 to 5 per cent.
Direct Taxes
- Efforts to simplify taxes, improve tax payer services, provide tax certainty and reduce litigation to be continued.
- Enhance revenues for funding development and welfare schemes of government.
- 58 per cent of corporate tax from simplified tax regime in FY23, more than two-thirds taxpayers availed simplified tax regime for personal income tax in FY 24.
Simplification for Charities and of TDS
- Two tax exemption regimes for charities to be merged into one.
- 5 per cent TDS rate on many payments merged into 2 per cent TDS rate.
- 20 per cent TDS rate on repurchase of units by mutual funds or UTI withdrawn.
- TDS rate on e-commerce operators reduced from one to 0.1 per cent.
- Delay for payment of TDS up to due date of filing statement decriminalized.
Simplification of Reassessment
- Assessment can be reopened beyond three years upto five years from the end of Assessment Year only if the escaped income is ₹ 50 lakh or more.
- In search cases, time limit reduced from ten to six years before the year of search.
Simplification and Rationalisation of Capital Gains
- Short term gains on certain financial assets to attract a tax rate of 20 per cent.
- Long term gains on all financial and non-financial assets to attract a tax rate of 12.5 per cent.
- Exemption limit of capital gains on certain financial assets increased to ₹ 1.25 lakh per year.
Tax Payer Services
- All remaining services of Customs and Income Tax including rectification and order giving effect to appellate orders to be digitalized over the next two years.
Litigation and Appeals
- ‘Vivad Se Vishwas Scheme, 2024’ for resolution of income tax disputes pending in appeal.
- Monetary limits for filing direct taxes, excise and service tax related appeals in Tax Tribunals, High Courts and Supreme Court increased to ₹60 lakh, ₹2 crore and ₹5 crore respectively.
- Safe harbour rules expanded to reduce litigation and provide certainty in international taxation.
Employment and Investment
- Angel tax for all classes of investors abolished to bolster start-up eco-system,.
- Simpler tax regime for foreign shipping companies operating domestic cruises to promote cruise tourism in India.
- Safe harbour rates for foreign mining companies selling raw diamonds in the country.
- Corporate tax rate on foreign companies reduced from 40 to 35 per cent.
Deepening tax base
- Security Transactions Tax on futures and options of securities increased to 0.02 per cent and 0.1 per cent respectively.
- Income received on buy back of shares in the hands of recipient to be taxed.
Social Security Benefits.
- Deduction of expenditure by employers towards NPS to be increased from 10 to 14 per cent of the employee’s salary.
- Non-reporting of small movable foreign assets up to ₹20 lakh de-penalised.
Other major proposal in Finance Bill
- Equalization levy of 2 per cent withdrawn.
Changes in Personal Income Tax under new tax regime
- Standard deduction for salaried employees increased from ₹50,000 to ₹75,000.
- Deduction on family pension for pensioners enhanced from ₹15,000/- to ₹25,000/-
- Revised tax rate structure:
| 0-3 lakh rupees | Nil |
| 3-7 lakh rupees | 5 per cent |
| 7-10 lakh rupees | 10 per cent |
| 10-12 lakh rupees | 15 per cent |
| 12-15 lakh rupees | 20 per cent |
| Above 15 lakh rupees | 30 per cent |
- Salaried employee in the new tax regime stands to save up to ₹ 17,500/- in income tax.