Researchers Achieve Breakthrough in Silicon-Compatible Magnetic Whirls
The work was led by Dr Hariom Jani from Oxford University’s Department of Physics working in Professor Paolo Radaelli’s research group, in collaboration with the National University of Singapore and the Swiss Light Source.
Dr Jani said: ‘Silicon-based computing is much too energy-inefficient for the next generation of computing applications such as full-scale AI and autonomous devices. Overcoming these challenges will require a new computing paradigm that utilises physical phenomena that are both fast and efficient to augment current technology.’
‘We have been looking at harnessing magnetic whirls in a special class of materials called antiferromagnets, which are 100-1000 times faster than modern devices. The problem to date has been that these whirls can only be created on rigid crystal templates that are incompatible with current silicon-based technology, so our goal was to figure out a way to translate these exotic whirls to silicon.’
‘To achieve this, we fabricated ultra-thin crystalline membranes of hematite (the main component of rust and thus the most abundant antiferromagnet) that extended laterally over macroscopic dimensions,’ explains Professor Radaelli. ‘Such membranes are relatively new in the world of crystalline quantum materials, and combine advantageous characteristics of both bulk 3D ceramics and 2D materials, while also being easily transferrable.’
The hematite layer was grown on top of a crystal template that was coated with a special ‘sacrificial layer’ made from a cement component. This sacrificial layer dissolved in water, separating the hematite easily from the crystal base. Finally, the free-standing hematite membrane was transferred onto silicon and several other desirable platforms.
Eventually, such devices could be integrated into new types of computers that work more like the human brain – we are very excited about what’s coming next.
Dr Hariom Jani, Department of Physics, University of Oxford
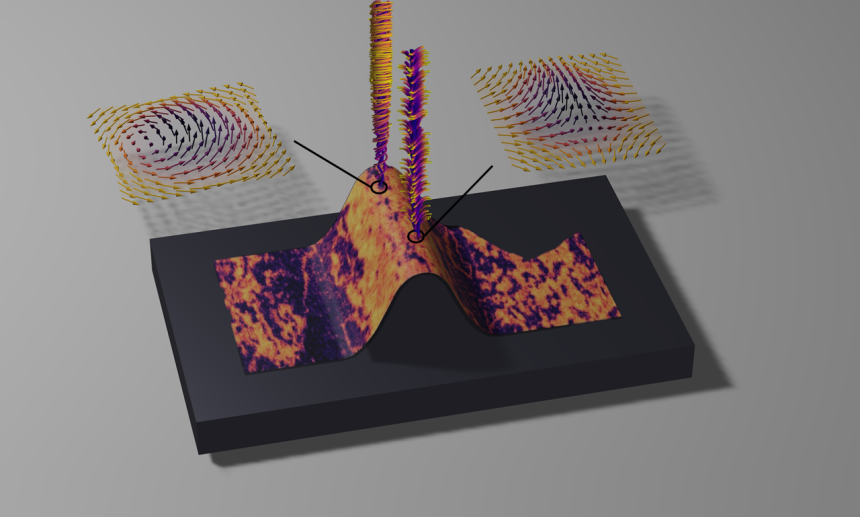
The group developed a novel imaging technique using linearly polarised X-rays to visualise the nanoscale magnetic patterns within these membranes. This method revealed that the free-standing layers are able to host a robust family of magnetic whirls. Potentially, this could enable ultra-fast information processing.
‘One of our most exciting discoveries was the extreme flexibility of our hematite membranes,’ continues Dr Jani. ‘Unlike their rigid, ceramic-like bulk counterparts that are prone to breaking, our flexible membranes can be twisted, bent, or curled into various shapes without fracturing. We exploited this newfound flexibility to design magnetic whirls in three dimensions, something that was previously not possible. In the future, the shape of these membranes could be tweaked to realise completely new whirls in 3D magnetic circuits.’
The group are now working on developing prototype devices that will use electrical currents to excite the rich dynamics of these super-fast whirls. Dr Jani concludes: ‘Eventually, such devices could be integrated into new types of computers that work more like the human brain – we are very excited about what’s coming next.’
The study ‘Spatially reconfigurable antiferromagnetic states in topologically rich free-standing nanomembranes’ has been published in Nature Materials.

